Unveiling the Landscape: Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
Research serves as the cornerstone of knowledge advancement. It propels us towards discovering new information and tackling intricate problems. Within this realm, researchers navigate two primary approaches: quantitative research and qualitative research.
Selecting the most suitable research method is crucial. It hinges on the research question, investigation goals, and available resources. This article delves into the key distinctions between quantitative and qualitative research, exploring their strengths, limitations, and appropriate applications.
Demystifying the Divide: Core Differences
The table below outlines the fundamental differences between quantitative and qualitative research approaches:
| Feature | Quantitative Research | Qualitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Quantify and measure variables, enabling generalization of findings to a broader population. | Gain a deep and meaningful understanding of the phenomenon under investigation, fostering the development of new theories. |
| Research Questions | Closed-ended and structured questions seeking “yes” or “no” answers. | Open-ended and dynamic questions that delve deeper into the phenomenon. |
| Data Collection Methods | Standardized tools like surveys, tests, structured observations, and statistical analysis. | Interviews, focus groups, participant observation, content analysis, and narrative analysis. |
| Data Analysis | Statistical analysis using statistical software. | Content analysis and interpretation of collected data. |
| Findings | Numbers, statistics, and graphs. | Descriptions, themes, and theories. |
Quantitative Research: Unveiling Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
- High level of accuracy and reliability
- Generalizability of findings to a larger population
- Ability to compare findings with other studies
- Utilization of statistical software for data analysis
Weaknesses:
- Limited ability to gain a deep and meaningful understanding of the phenomenon
- Requirement for standardized and potentially expensive data collection tools
- Inability to adapt to changing circumstances
- Risk of bias in study design and data analysis
Qualitative Research: Exploring Advantages and Limitations
Strengths:
- Provides a deep and meaningful understanding of the phenomenon
- Adapts to evolving situations
- Uncovers new and unexpected findings
- Enables active participation of participants in the research process
Weaknesses:
- Lower level of accuracy and reliability
- Difficulty in generalizing findings to a larger population
- Demand for specialized skills in data collection and analysis
- Potential for bias in the interpretation of findings
Choosing the Right Path: Applications of Each Approach
Quantitative research excels in studies aiming to measure variables, determine relationships between variables, and generalize findings to a larger population. Examples include survey studies, experimental trials, and big data analysis.
Qualitative research flourishes in studies seeking a deep and meaningful understanding of complex phenomena, individual experiences and perspectives, and the generation of new theories. Examples include case studies, in-depth interviews, participant observation, and narrative analysis.
The optimal research method hinges on the research question, investigation goals, and available resources. In some instances, researchers might employ both quantitative and qualitative approaches in tandem. This is known as mixed methods research.
The Road Ahead: Combining Insights for a Robust Research Journey
Ultimately, researchers must carefully consider the nature of their study to determine the most suitable research method. Here are some additional tips for navigating this decision:
- Clearly define your research question and objectives. This will guide you towards the approach that best aligns with your goals.
- Consider the nature of your data. Quantitative research is suited for numerical data, while qualitative research is suited for textual or observational data.
- Evaluate your resources. Quantitative research often requires specialized software and potentially expensive data collection tools.
- Acknowledge the limitations of each approach. No single method is perfect. Understanding the limitations of your chosen approach allows you to mitigate potential biases and strengthen your research design.
By understanding the distinctions between quantitative and qualitative research, their strengths and weaknesses, and their appropriate applications, researchers can embark on a more informed and effective research journey.
The two types of research including quantitative and qualitative refers to the type of data used in the research. Generally, if the data is numerical, it is quantitative. Otherwise, it is qualitative.
Qualitative research
With this in mind, it is obvious that qualitative researches usually study human behavior and other phenomena which is not measurable. It helps to develop ideas or hypotheses. The parallel researches for this kind of research can be empirical, exploratory, investigative, case studies, and subjective research.
Research questions
The research questions are often “how” and “why” something happens. It can establish cause and effect relationships.
Methodology
The methods of data collection could be interview, observation, or documents (including books, papers, and so on). So the qualitative methods use unstructured or semi-structured techniques.
Data analysis and results
In order to analyze data, the data should be described, compared, and the results reported. Qualitative researches aim for discovering patterns or possible links between variables.
Quantitative research
Quantitative researches study the facts, science, and society. Quantitative research mostly is experimental like applied behavioral analysis, and non-experimental like surveys, causal-comparative and correlational researches.
Quantitative researches are objective because they use numerical data which relates to mathematics that is an objective science, and because of this characteristic, the results will be generalizable.
Quantitative researches are useful for testing and validating theories constructed through qualitative researches.
Research questions
Quantitative research tries to solve a problem. So the research questions come from the gaps in prior researches. For example, it will be useful to find out the statistical correlation, or the effects of something.
Methodology
The methods of data collection are using questionnaires, controlled observations, and other measurable methods. So the data is numerical or can be transported into statistics. For example, it can be put into categories. It is more structured than qualitative research data.
In order to conduct quantitative research, you need a sample which needs to be of a large size so that the research be reliable.
Data analysis and results
Since the data are in numerical form, it can be analyzed by statistical methods and software and the results can be reported in the form of graphs, tables, etc. as well as a description of them.
The mixed method
Today using the combination of qualitative and quantitative researches is increasing. In fact, these two kinds of research are not opposite, but they are of two different philosophies.
In research that combines the two types of researches, the elements of both can be used. The results also is a combination of why and what. So you can gain much deeper insights.
The uses of mixed method
Mixed method is useful especially for market researches. Since when you interview with people (qualitative research) you can be aware of their emotional, the lacks they feel your product/ service has, etc. while, with the help of a questionnaire (quantitative research) you have a statistical and exact result of your customers’ satisfaction.
The following table has been borrowed from “Research Design” book by “Creswell” which compares the three approaches:
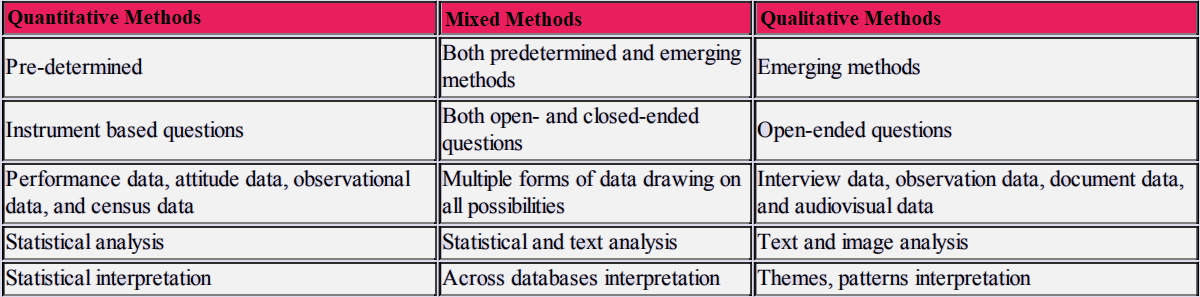 quantitative, mixed, and qualitative methods
quantitative, mixed, and qualitative methods
Questions and Answers about “Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research”
1. What is the main difference between quantitative and qualitative research?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research lies in the nature of the data they collect and the type of analysis they perform:
- Quantitative research focuses on collecting numerical data and applying statistical methods to analyze it. It aims to quantify the problem and often uses surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection tools.
- Qualitative research involves collecting non-numerical data, such as interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys. It focuses on understanding experiences, behaviors, or phenomena in-depth.
2. What are the goals of quantitative research?
The goal of quantitative research is to quantify the problem by generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into usable statistics. Researchers aim to identify patterns, relationships, or trends and test hypotheses. It is often used to establish generalizable findings across larger populations.
3. What are the goals of qualitative research?
The goal of qualitative research is to explore and understand people’s experiences, motivations, and perspectives in a detailed and descriptive manner. Researchers aim to generate rich, contextual data that provides insight into the underlying reasons and social phenomena.
4. How is data collected in quantitative research?
Data in quantitative research is collected through structured methods like surveys, questionnaires, experiments, or observational studies. The data is often numeric and can be analyzed using statistical techniques to test hypotheses or determine correlations.
5. How is data collected in qualitative research?
In qualitative research, data is often collected through unstructured or semi-structured methods such as interviews, focus groups, observations, or document analysis. The data is non-numerical and typically takes the form of text, audio, or video, which is analyzed for patterns, themes, and meanings.
6. What are the types of data in quantitative research?
Quantitative research uses numerical data, which can be further classified into:
- Discrete data: Data that can be counted (e.g., number of students in a class).
- Continuous data: Data that can take any value within a range (e.g., height, weight, temperature). This data is often measured on a scale or in categories and can be analyzed using statistical methods.
7. What are the types of data in qualitative research?
Qualitative research uses non-numerical data, which can include:
- Textual data: Such as transcripts from interviews or written responses.
- Audio/visual data: Such as recordings or videos of interviews and focus groups.
- Observational data: Descriptions of behaviors or events. This data is analyzed thematically or narratively to identify patterns or meanings.
8. What is the role of hypotheses in quantitative research?
In quantitative research, hypotheses play a central role. Researchers typically start with a clear hypothesis (or hypotheses) that they aim to test through statistical analysis. Hypotheses are predictions about the relationships between variables, and the goal is to confirm or refute these hypotheses using data.
9. What is the role of hypotheses in qualitative research?
Qualitative research typically does not start with a formal hypothesis. Instead, the research often begins with broad research questions or themes, and the aim is to explore the phenomenon in-depth. Hypotheses may emerge during data collection or analysis as patterns and themes become apparent.
10. How is the data analyzed in quantitative research?
Data analysis in quantitative research involves statistical techniques to test hypotheses, identify correlations, and make predictions. Researchers use tools such as SPSS, R, or Excel to conduct descriptive statistics (e.g., mean, median) and inferential statistics (e.g., t-tests, regression analysis) to analyze the data.
11. How is the data analyzed in qualitative research?
In qualitative research, data is analyzed using methods like thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory. Researchers look for recurring themes, patterns, or narratives within the data. Tools like NVivo or Atlas.ti may be used to organize and code data, but the analysis is more interpretive than statistical.
12. What is the level of objectivity in quantitative research?
Quantitative research strives for a high level of objectivity. Researchers aim to minimize bias through controlled experiments and statistical analysis. The focus is on replicability and generalizability, which ensures that results can be verified by others in similar settings.
13. What is the level of objectivity in qualitative research?
Qualitative research, while striving for rigor, often involves a higher degree of subjectivity due to the nature of human interpretation. Researchers analyze data based on their own perspectives and understanding, but efforts are made to ensure trustworthiness through methods like triangulation, member checking, and reflexivity.
14. Can quantitative and qualitative research be combined?
Yes, mixed-methods research combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Researchers may collect both numerical data and qualitative data to provide a fuller picture of the research problem. This approach allows for the strengths of both methods to complement each other.
15. Which research method is more suitable for exploratory studies?
Qualitative research is more suitable for exploratory studies, where the aim is to explore a topic, identify patterns, or understand underlying processes. It is particularly useful when little is known about the topic, and researchers want to gain a deeper understanding.
16. Which research method is more suitable for testing a theory?
Quantitative research is typically more suitable for testing theories or hypotheses. By using statistical analysis, researchers can validate or invalidate theoretical propositions through structured data collection and analysis.
17. How does sampling differ between quantitative and qualitative research?
In quantitative research, sampling is typically larger and aims to be representative of a broader population to ensure the generalizability of findings. Random or stratified sampling techniques are commonly used.
In qualitative research, sampling is smaller and more purposive, with participants selected based on their knowledge or experience of the topic. The focus is on depth rather than breadth.
18. Which method provides more generalizable results?
Quantitative research generally provides more generalizable results because it involves larger sample sizes and statistical analysis, allowing researchers to make conclusions about larger populations.
Qualitative research, on the other hand, provides in-depth insights but is less generalizable due to smaller sample sizes and a focus on specific contexts.
19. Can qualitative research be used in hypothesis testing?
Qualitative research is typically not used for hypothesis testing in the same way as quantitative research. However, qualitative data can help to generate hypotheses or explore the context in which a hypothesis might apply, providing a foundational understanding before quantitative testing.
20. What are the strengths of quantitative research?
The strengths of quantitative research include:
- Ability to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Data can be generalized to a larger population.
- Provides clear, objective, and replicable results.
- Facilitates statistical analysis to identify trends and patterns.
21. What are the strengths of qualitative research?
The strengths of qualitative research include:
- Provides rich, detailed, and deep insights into a phenomenon.
- Can explore complex social and human experiences.
- Flexible and adaptable to new findings as they emerge.
- Useful for developing theories or understanding context and meaning.