Bridging Cultures: A Guide to Arabic Translation
The Arabic language, with its rich history and diverse dialects, serves as a vital link across cultures and regions. For businesses, organizations, and individuals seeking to connect with the Arabic-speaking world, effective translation is paramount. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of Arabic translation, equipping you with the knowledge and resources to navigate this multifaceted field.
The Nuances of Arabic Translation
Arabic translation goes beyond simply converting words from one language to another. Here’s why it demands a nuanced approach:
- Dialectical Variations: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) serves as the formal written language, but numerous spoken dialects exist across the Arabic-speaking world (e.g., Egyptian Arabic, Levantine Arabic, Moroccan Arabic). Translators must understand the target audience and dialect to ensure clear communication.
- Cultural Context: Language is intricately linked to culture. Effective translators recognize cultural nuances and sensitivities to avoid misunderstandings or misinterpretations in the translated text.
- Terminology and Jargon: Technical fields like medicine, law, or engineering have specialized vocabulary that requires meticulous translation to ensure accuracy and maintain the intended meaning.
- Literary Devices and Stylistic Choices: Translating literary works presents an additional challenge. Translators must capture the essence of the original text, including the author’s voice, wordplay, and figurative language.
Types of Arabic Translation
The type of Arabic translation required depends on the purpose and target audience. Here’s an overview of some common categories:
- Localization: This involves adapting content to a specific Arabic dialect and cultural context. It often goes beyond word-for-word translation, modifying elements like humor, idioms, and references for cultural appropriateness.
- Sworn Translation: Official documents like legal contracts, birth certificates, or academic transcripts require certified translations by qualified professionals. These translations hold legal weight and must be accurate and verifiable.
- Website Localization: Translating websites for the Arabic market requires attention to user interface (UI) elements, ensuring a seamless user experience for Arabic speakers. Text directionality (right-to-left in Arabic) and cultural sensitivity are crucial considerations.
- Literary Translation: Translating novels, poems, or other literary works demands a deep understanding of the source language and the ability to convey the author’s style, tone, and literary devices effectively in the target Arabic dialect.
Finding the Right Arabic Translator
Selecting a qualified Arabic translator is crucial for ensuring the success of your project. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Expertise and Experience: Look for translators with experience in your specific field of translation (e.g., legal, technical, or literary).
- Native Proficiency: Ensure the translator has a native-level command of both Arabic and your source language.
- Cultural Understanding: Choose a translator familiar with the target audience’s cultural context to avoid potential misinterpretations.
- Translation Process: Inquire about the translator’s workflow, including quality control measures and revision processes.
- Certifications: For sworn translations, select a translator who is certified to provide legally binding translations.
- Cost and Timelines: Obtain quotes and estimated timelines to ensure the service aligns with your budget and project deadlines.
Additional Resources for Arabic Translation
- Professional Translation Associations: Organizations like the American Translators Association (ATA) or the Arabic Translators Association (ATA) offer resources and directories of qualified translators.
- Machine Translation Tools: Free and paid machine translation tools like Google Translate can be helpful for basic understanding but should not be used for professional translations.
- Online Translation Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to Arabic translation can be a valuable resource for finding translators, asking questions, and learning more about the field.
The Future of Arabic Translation
The world of Arabic translation is constantly evolving. Here are some emerging trends to keep an eye on:
- Machine Translation Advancement: While machine translation cannot replace human expertise, advancements in artificial intelligence may lead to more accurate and nuanced machine translation tools in the future.
- Increased Demand for Translation Services: As globalization continues, the demand for high-quality Arabic translation services is likely to rise across various industries.
- Focus on Cultural Sensitivity: Translators will need to be even more adept at navigating cultural nuances and ensuring translated content resonates effectively with the target audience.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Arabic Translation
Effective Arabic translation has the power to break down language barriers and foster communication across cultures.
If you google “Arabic translation” so many online translation websites would be listed, offering Arabic to English, English to Arabic, etc. translations.
The best of these machines do the translation based on some formulas, while most of them do a word for word translation that results in a vague text.
Now imagine the time when a person does the translation. He/she would choose definition of words wisely, in a way that the meaning matches rest of the sentence and the final text has a clear meaning, it is understandable, and transfers some meaningful data to the readers.
If the translator be a professional one, the translation would be of coherent and cohesion. A professional translator even may does some researches to understand the original text, then translate it in a way that be completely clear and understandable to the audience.
Difficulties in Arabic translation
Arabic is of two different kinds: classical Arabic, which is the language used in Quran and in formal writings, and the other one is modern Arabic, which is used in modern texts and in speaking. So in order to translate a text into Arabic you need to know who the audience is.
In addition, it is assigned gender to each Arabic word. For example the sun, the earth, tables, and all the things and even verbs have a gender. It makes the translator to be careful in using verbs and pronouns.
Furthermore, modern Arabic has a wide range of dialects. It adds another difficulty in translating Arabic.
Differences between English and Arabic
When you are writing Arabic, you starts from the right side of a line and ends in the left.
Besides Arabic alphabet is completely different from Latin alphabet.
As it was said, verbs and things are assigned gender which in English language does not matter.
Despite all these differences, some English words rooted in Arabic, e.g. “guitar” which is “qithara” in Arabic.
Conclusion
As Google suggests, Arabic is the second most difficult language to translate, after Mandarin.
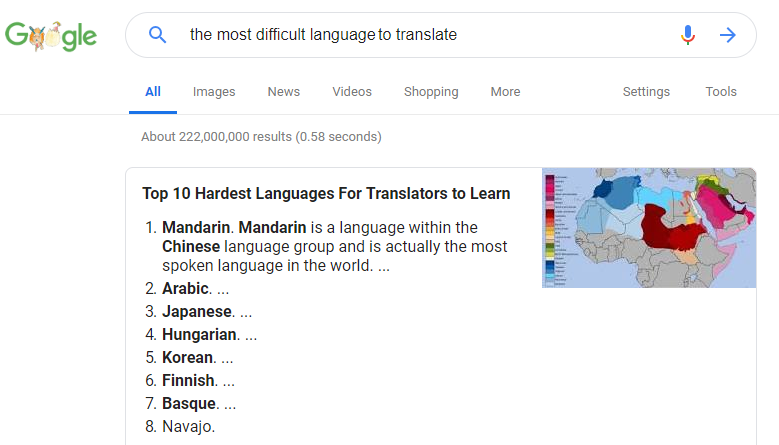
So translating texts specially academic texts and papers is very important and needs a precision, experienced translator who is interested in his/her work and does researches in case in is necessary so that the final translation be an accurate, clear, and easy to understand text.
One of the Hoortash’s services is translation services. Our translators offer professional and specialized translations in Arabic, English, and Russian.






Hello, Your Arabic translation blog is amazing for everyone and very informative for me. I am also a translator at Acadetudio. Acadestudio provides multiple language translation services. If you require any language services please contact.