Design of a research study is the procedures a researcher go through for answering the research questions. It includes two phases: the collecting data method and analyzing it.
Design of a research study depends on the variables and the type of the study or research as it was mentioned in “chapter 3”. The type of research can be qualitative, quantitative, or a mixture of both. So in order to choose an appropriate design of a research study, you need to find out the type of your research.
Different types of research studies
The three different types of research studies were discussed in “qualitative research vs. quantitative research”. In short,
Qualitative research studies immeasurable phenomena. Their function is to develop ideas.
Quantitative researches are using numerical data. These studies are used for testing and validating theories. In other words, they answer qualitative research questions.
The mixed method, as the name suggests, is a mixture of qualitative and quantitative research. These kinds of studies apply both numerical and non-numerical instruments. For example, a study using a questionnaire as a numerical instrument and observation as a non-experimental instrument would need a mixed method design.
So in order to choose an appropriate design of a research study, the first thing you need to do is to recognize the type of your study.
Types of research design
Quantitative studies
Major types of research design regarding quantitative studies are experiments and non-experiments each includes some minor types and follows a standard format.
– Data collection procedure
In quantitative designs, the researcher chooses a sample and studies them. The results will be generalized to all the population. There are numerous ways of sampling like random sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling, etc.
– The instruments
Then the data related to each variable will be collected through the appropriate instrument. The instruments used for a survey are questionnaires. Sometimes there are readymade questionnaires and sometimes the researcher develops one.
– Data analysis
After the data gathered, it is time to analyze the data. Sort the data in tables and find the mean, standard deviation, the shape of SD graph (bell shape, curved shape, etc.), and range of scores for all the variables as well as the reliability and the statistical procedure of the instruments. The research questions have to be answered in this section by the use of gathered data and statistical procedures. Taking advantage of graphs, tables, and figures also help you with that. Write a descriptive data analysis based on the obtained information.
Qualitative studies
– Data collection procedure
A most specific characteristic of qualitative studies is that the study occurs in a natural field. They do not sample or experiment a phenomenon in a lab, but go through nature, the people, and generally what/whom the study is about (the subject).
– The instruments
In qualitative designs, the researcher uses multiple sources to collect data such as different documents, observation, interviews, protocols, etc.
Despite the quantitative design that uses questionnaires and even most of the time uses ready-made questionnaires, the qualitative design does not use any instrument made by other researchers.
In fact, the qualitative design of a research study is so flexible. The researcher can study different fields, applies different instruments, and even the instruments are not definite but they can be changed or added during the procedure. For example, the questions the researcher asks in an interview are not following an exact form.
– Data analysis
In a qualitative design of a research study, the researcher needs to employ inductive and deductive data analysis together.
s/he once concludes from the gathered information. In other words, s/he reaches to a conclusion from small pieces of information which is deductive mode.
Then s/he analyzes the whole or theme to reach to the specific characteristic of the population.
Generally, the researcher should investigate the abstract and concrete information in different forms; from abstract to concrete and vice versa, from theme to characteristics and vice versa. s/he should assess the topic from different aspects and different facets.
Mixed method
Obviously, each method including qualitative and quantitative designs has its defects. While by borrowing the strengths of methods, proposing a better method is possible. Mixed method is the method which is produced by combining the strengths of the other ones.
– Data collection procedure
In the mixed method, in order to answer the research questions, both qualitative and quantitative data should be collected. So it employs both sampling and nature to gather the information.
– The instruments
Since the method is a mixture of the others, the researcher is allowed to use questionnaires as well as documents, observation, interviews, etc. depending on the subjects under investigation and the topic of research.
The data related to each variable should be collected using the appropriate instrument. The choices need to be rational and supported by theories suggested by other researchers.
It is better to use the documents, audio/visual materials, observe, then interview and finally make use of questionnaires. In other words, at first employ the qualitative design instruments and after that go to quantitative method ones which is questionnaires.
– Data analysis
As the type of this method suggests, data analysis would be a mixture of the qualitative data analysis and quantitative analysis.
Even the quantitative data can be analyzed through the qualitative data analyses method, after evaluating the statistical scores and sorting them in tables and graphs. In other word, after analyzing the quantitative data as it was said in its section, the researcher should analyze the results regarding all the variables using qualitative data analysis.
Summary
You can see a summary of this post in the following table:
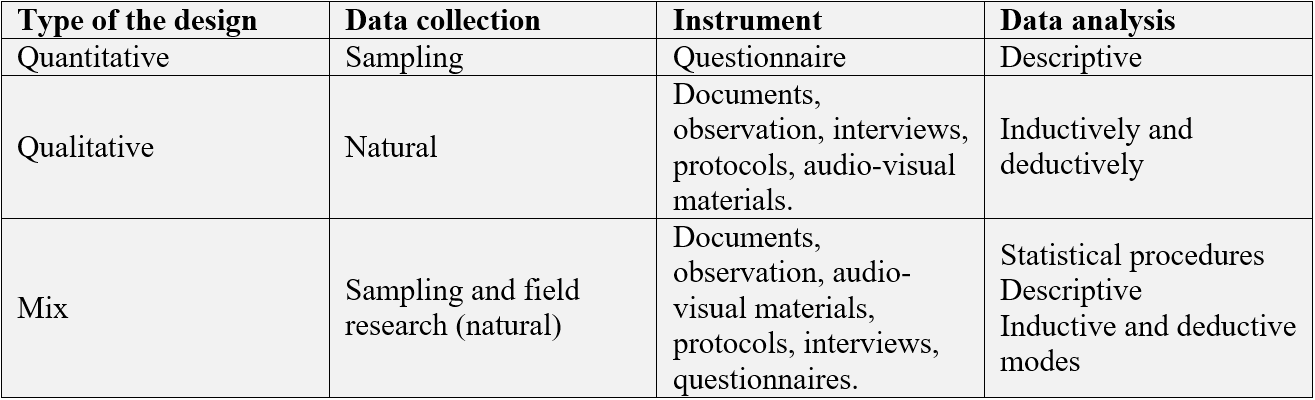 types of the design
types of the design
Questions and Answers about “Design of a Research Study”
1. What is the design of a research study?
The design of a research study is the framework or blueprint that guides how the research will be conducted. It includes the methods, procedures, and techniques used to collect and analyze data.
2. What are the main types of research study designs?
The main types include:
- Descriptive: Observes and describes characteristics or phenomena.
- Exploratory: Investigates new or poorly understood topics.
- Experimental: Tests hypotheses through controlled experiments.
- Correlational: Examines relationships between variables.
- Longitudinal: Studies subjects over an extended period.
3. Why is the design of a research study important?
A well-structured design ensures:
- Systematic and organized data collection.
- Valid and reliable results.
- Minimization of bias and errors.
- Clear alignment with research objectives.
4. What are the key elements of a research design?
The key elements include:
- Research question or hypothesis.
- Study population and sample size.
- Data collection methods.
- Variables and measurements.
- Data analysis techniques.
- Ethical considerations.
5. How do I choose the appropriate research design?
Consider the following:
- Your research objectives and questions.
- The type of data you need (qualitative or quantitative).
- Available resources and time constraints.
- The study’s ethical requirements.
6. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research designs?
- Qualitative: Focuses on understanding concepts, experiences, or phenomena through non-numerical data like interviews and observations.
- Quantitative: Involves numerical data to test hypotheses and measure relationships between variables.
7. What is a mixed-methods research design?
A mixed-methods design combines qualitative and quantitative approaches in a single study to gain a comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
8. What is the role of sampling in research design?
Sampling involves selecting a subset of the population for study. It ensures that the sample represents the larger population, making findings generalizable and accurate.
9. How does experimental design differ from observational design?
- Experimental design: Researchers manipulate variables and observe outcomes in a controlled environment.
- Observational design: Researchers observe and analyze variables without intervention.
10. What are the common types of experimental designs?
- Pre-experimental: No control group.
- Quasi-experimental: Has a control group but lacks randomization.
- True experimental: Includes randomization and control groups.
- Factorial design: Studies multiple variables simultaneously.
11. How can I ensure validity in my research design?
To ensure validity:
- Clearly define variables.
- Use reliable measurement tools.
- Avoid bias through randomization and blinding.
- Test your methods through pilot studies.
12. What are some examples of descriptive research designs?
Examples include:
- Surveys.
- Case studies.
- Observational studies.
- Content analysis.
13. How does ethical consideration influence research design?
Ethical considerations ensure that research respects participants’ rights, including informed consent, confidentiality, and minimizing harm. They also guide how data is collected and stored.
14. What is the difference between cross-sectional and longitudinal designs?
- Cross-sectional: Collects data at a single point in time.
- Longitudinal: Collects data over a period to observe changes or trends.
15. How does a pilot study relate to research design?
A pilot study tests the feasibility of your research design, identifying potential issues and allowing adjustments before the full study.
16. What is the role of data analysis in research design?
Data analysis involves examining collected data to answer research questions, test hypotheses, or generate new insights. It must align with the study’s objectives and chosen design.
17. Can research design evolve during the study?
Yes, in some cases, especially in exploratory or qualitative research, designs may adapt to new findings or challenges encountered during the study.
18. What tools are used to create a research design?
Tools include:
- Statistical software (e.g., SPSS, R, Python for quantitative studies).
- Qualitative analysis tools (e.g., NVivo, MAXQDA).
- Survey platforms (e.g., Google Forms, SurveyMonkey).
19. How does a well-designed study address limitations?
A well-designed study identifies potential limitations (e.g., sample size, data availability) and incorporates strategies to mitigate their impact, such as triangulation or sensitivity analyses.
20. What are some common mistakes in research design?
Common mistakes include:
- Unclear research questions.
- Poorly defined variables.
- Insufficient sample size.
- Bias in data collection methods.
- Lack of ethical compliance.
These questions and answers provide a clear overview of research study design, its importance, and practical considerations for researchers.