In previous posts, we explained the differences between qualitative and quantitative researches. We also discussed how to write chapter 1 and chapter 2 in a thesis. They both follow the same format in qualitative and quantitative researches, and in “how to write chapter 3 of a
As it was noted before, every university and institute has its rule of thesis writing and you should adhere to them, but the point is that most of them are the same in major parts. So this guide will be helpful to everyone studying/ working in every institute. Just do not forget to apply them in your thesis, too.
Chapter 3 of every thesis is “the methodology” chapter, which means you need to explain the methods and techniques you have used in order to collect data to answer the research questions.
The sections of this chapters includes:
3.1 introduction
3.2 design of the study
3.3 data collection techniques
3.4 instrumentation
3.5 informants/ sampling
3.6 data analysis
3.7 ethical consideration
As the content of chapter 3 of a qualitative thesis, the names of each section may have small differences in different universities. You need to follow your university/ institute’s rules.
3.1 introduction
Each chapter of research or thesis needs an introduction as well as a summary.
The introduction of chapter 3 of a qualitative thesis is the same as quantitative thesis, i.e. it is of two parts. The first one reviews the goals of the study, the research questions,
3.2 design of the study
The design of the study determines the way the study will be conducted. You need to write it comprehensively so that who is to repeat the research or put your study as a base for her study knows how to do the research.
By the design of a study, we mean the strategies the researcher choose to answer the research questions related to each variable.
The design of qualitative research can be one of the strategies shown in the below picture:
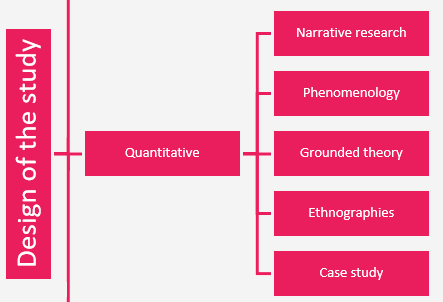
As well as naming the strategy you have chosen, support your choice by logical reasons. The reasons need to be convincing.
You do not need to explain what the strategy is. But describe how it is used in relation to your study step by step.
3.3 data collection techniques
In qualitative research, you can collect the needed data through an
You can make use of one or more of them. Do not just name the technique, explain why you chose this technique and not the other one.
3.4 instrumentation
In this section clarify how you used the chosen technique/s. For example, if you interviewed people, explain what kind of questions have been asked, were they structured or not, and give some examples. Again be clear enough so that other researchers can follow and repeat what you have done.
3.5 informants/ sampling
In this section answer the questions related to the way you collected data which may raise in reader’s mind, such as how many questions were asked, how the interviewees were chosen, and basically how you choose the informants.
Support each of them by convincing reasons.
3.6 data analysis
In this part you need to organize, interpret, and find a pattern in the collected data. For example, you may identify an explanation for the phenomenon you are searching on, or find out a relationship between the variables of your thesis.
There are two approaches to qualitative data analysis which are deductive approach and inductive approach. Again you do not need to explain the approach in your thesis, just mention that and apply it to analyze the qualitative data of your thesis.
3.7 ethical consideration
Any document that proves you have collected the data legally and ethically e.g. preserving animal rights, the privacy policy, or any other letters regarding the subject of your research.




