In previous posts, we discussed writing chapter one and writing chapter two. In this post, we will see how to write chapter 3 of a quantitative thesis.
As the name implies, in chapter 3 of a thesis or dissertation, you need to write about the methods you have used in order to conduct the research and evaluate the variables. Unlike chapters 1 and 2, there are slight differences between writing chapter 3 for qualitative and quantitative researches.
Before everything else, by methodology, we mean the way you choose to find out answers to the research questions. These ways are called techniques and are specified. The only thing you need to do is to choose the most appropriate technique considering your research philosophy. Then, in chapter five of thesis or in methodology chapter explain it in detail and clarify how you designed your research.
The subsections of chapter 3 of a quantitative research includes:
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Participants
3.3 Instrumentation / Instruments
3.4 Design of the study
3.5 Data collection procedure
3.6 Data analysis procedure
3.7 Variables (optional)
3.8 Materials and instruments (optional)
3.9 The research site (not in all researches)
Pay attention that different universities have different forms for writing each chapter, however, they are not major differences. Probably the position of information differs but the main content does not differ.
Now we are going to introduce and explain each of the subsections one by one:
3.1 Introduction
As you may understand till now, each chapter begins with an introduction which is explaining what is going to be discussed in the chapter. Because of such content, the introduction part in each chapter will be written when the whole chapter is written.
In the introduction of chapter 3 of a quantitative thesis, firstly, remind the readers about the research questions and hypotheses, the problem or gap, and the purpose of the study. Secondly, relate them to subsections of chapter 3. Give the readers a brief look over what they are going to read e.g. write about the questionnaires, number of the questions, validity, reliability of each questionnaire, and so on, in brief.
Avoid repeating the exact phrases of research questions, hypotheses, etc. rephrase them and note that it is to be a reminder.
3.2 Participants
Explain who your participants are, as specific as you can. For example, you may include the number of samples, the method of choosing them, and so on.
3.3 Instrumentation / Instruments
In research, the variables should be evaluated; the question is how did you evaluate them in your research. What method you have chosen to evaluate each variable; write on each variable in a separate subsection, and number it like 3.3.1, 3.3.2, and so on.
In each subsection write about the instrument you used to evaluate the variable. At first, prove that the chosen instrument is valid and reliable for your research, then explain about the instrument itself, in details. Explain things like how does it work, how the results are interpreting, what parts make it, and so on.
If the instrument you used is a questionnaire, attach them as “appendix” to the end of your thesis after “references” part.
3.4 Design of the study
As we said in “qualitative vs. quantitative research” a study could be of a qualitative, quantitative, or a mixed method design. The design of a study depends on the type of research.
After defining the design of the study, many other components of the research will be clarified, such as the type of instruments can be used in the study, the kinds of variables and research questions, the way the data should be analyzed and many other things. So it is very important to define the design of the study, it is a base for the research.
In “Research Design” book by “Creswell” you can find more detailed information on this part.
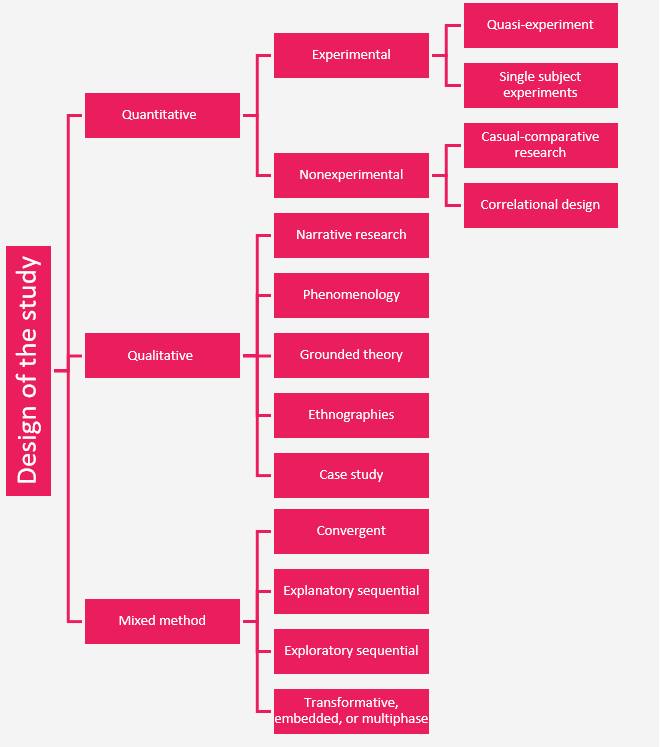
In this section, you need to explain the reasons for choosing the “experimental design” and why not “non-experimental design” (or vice versa).
then specify what kind of experimental/ non-experimental design you will use and – like other parts of this chapter – explain the reasons for your choice with regard to the goal of the study.
3.5 Data collection procedure
Ones may decide to replicate your research, so s/he will need the procedure of the study. Hence you need to explain how you collected the data in details. For example, where you collected the data, how you did it, what your data was, how you chose it, and so on.
3.6 Data analysis procedure
By data analysis procedure we mean the statistical test you have used to analyze the data, such as ANOVA, T-test, etc.
3.7 Variables
This part is optional. You may write the variables of the study and their types in this part.
3.8 Materials and instruments
This is optional too. If you have used a specific instrument or material in the research, it can be mentioned in this part. Note that it differs from the Instruments part in section 3.3. and refers to specific instruments or details.
3.9 The research site
In some researches, you need to mention the city where the study has been conducted.
Some other considerations
Note that these parts may differ in different universities, but the main idea does not change.
In some fields, such as pure science, or in some certain types of study like surveys these parts would be different.
In those kinds of majors which may not be empirical, the researcher just needs to discuss the study’s variables separately, in chapter 3. More details depend on your research and major. For example, you may write on a theory, so in chapter 3 you need to prove the accuracy of it.
Here are some questions and answers about “How to Write Chapter 3 of a Quantitative Thesis”:
1. What is the purpose of Chapter 3 in a quantitative thesis?
Answer: Chapter 3 in a quantitative thesis is typically dedicated to the methodology. The purpose of this chapter is to clearly explain the methods and procedures used to conduct the research. It should outline the research design, data collection methods, sampling strategies, and the statistical techniques or models employed to analyze the data.
2. What should be included in the methodology section of Chapter 3?
Answer: The methodology section of Chapter 3 should include:
- Research Design: The overall framework and approach (e.g., experimental, correlational, descriptive).
- Population and Sample: The target population, sampling techniques, sample size, and inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Data Collection: The instruments and tools used to gather data (e.g., surveys, questionnaires, tests).
- Data Analysis: The statistical methods and techniques used to analyze the data (e.g., regression analysis, ANOVA, correlation).
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical concerns, including consent, confidentiality, and how ethical guidelines were followed.
3. How do you explain the research design in Chapter 3?
Answer: In Chapter 3, you need to explain the type of research design used in the study (e.g., experimental, quasi-experimental, survey, observational). You should describe why this design was chosen, how it suits your research questions, and the advantages and limitations associated with it. It’s important to justify the choice of research design in the context of your study’s goals and objectives.
4. How do you choose the appropriate data collection method for a quantitative thesis?
Answer: Choosing the appropriate data collection method depends on the research questions, objectives, and type of data needed. Common methods in quantitative research include:
- Surveys/Questionnaires: Used for collecting numerical data on attitudes, behaviors, or characteristics.
- Experiments: For controlled studies where variables are manipulated.
- Tests/Assessments: For measuring specific traits or abilities.
- Secondary Data: Using pre-existing data, such as government reports or databases.
Each method should be clearly described in Chapter 3, with an explanation of why it’s appropriate for the research goals.
5. What is sampling, and why is it important in a quantitative thesis?
Answer: Sampling refers to selecting a subset of individuals from a larger population to participate in the study. In Chapter 3, you need to explain the sampling strategy, including:
- Sampling Method: Whether it’s random, stratified, convenience, etc.
- Sample Size: How many participants were selected, and how this number was determined.
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Who is eligible or not eligible to participate in the study.
Sampling is crucial because it impacts the generalizability of the results and ensures that the sample represents the population you’re studying.
6. What statistical methods should be included in Chapter 3 of a quantitative thesis?
Answer: In Chapter 3, you should provide a detailed explanation of the statistical methods you will use to analyze the data. Common techniques in quantitative research include:
- Descriptive Statistics: Mean, median, mode, standard deviation.
- Inferential Statistics: T-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis, correlation.
- Advanced Statistical Methods: Structural equation modeling (SEM), factor analysis, path analysis.
It’s important to justify your choice of statistical methods, explaining how they are suitable for addressing your research questions.
7. How do you explain the data analysis process in Chapter 3?
Answer: The data analysis section of Chapter 3 should describe:
- The software used: Mention which software was used for analysis (e.g., SPSS, R, Stata).
- The steps taken in analysis: How the data were cleaned, coded, and processed.
- Statistical tests and procedures: Specific tests that will be used to analyze the data (e.g., hypothesis testing, regression models).
- Assumptions and limitations: Any assumptions made during the analysis and how they could affect the results.
This section should be detailed enough to allow another researcher to replicate the study.
8. What ethical considerations should be addressed in Chapter 3?
Answer: Ethical considerations are an essential part of quantitative research. In Chapter 3, you should address:
- Informed Consent: How participants were informed about the study and gave consent.
- Confidentiality: How participants’ data will be kept confidential and secure.
- Right to Withdraw: Ensuring participants can withdraw from the study at any time without consequences.
- Approval: Any ethics review or approval from institutional review boards (IRB) or ethics committees.
These ethical issues must be clearly outlined to ensure the integrity of the research process.
9. How do you ensure validity and reliability in your quantitative thesis?
Answer: Validity and reliability are critical to the quality of quantitative research. In Chapter 3, you should describe:
- Reliability: How you ensured that the measurement tools are consistent and produce stable results over time (e.g., test-retest reliability, internal consistency).
- Validity: How you ensured that your instruments actually measure what they are intended to measure (e.g., construct validity, criterion-related validity).
It’s important to provide details on how you tested these aspects or if any previous studies validated your instruments.
10. How should you present the limitations of your methodology in Chapter 3?
Answer: In Chapter 3, you should acknowledge any limitations in your methodology. These could include:
- Sampling Issues: Small sample size, non-random sampling, or biases in selection.
- Measurement Limitations: Potential issues with the data collection instruments or their appropriateness for the research.
- Generalizability: How the findings may or may not apply to the larger population or different contexts.
Acknowledging limitations shows that you have a critical understanding of the research process and helps readers assess the validity of your findings.
11. How do you structure Chapter 3 of a quantitative thesis?
Answer: Chapter 3 is typically structured as follows:
- Introduction: Briefly introduce the chapter and its purpose.
- Research Design: Explain the overall design of the study.
- Sampling: Describe the sample and sampling methods.
- Data Collection: Discuss the instruments and procedures used to collect data.
- Data Analysis: Explain the statistical methods and tools used to analyze the data.
- Ethical Considerations: Outline the ethical aspects of your research.
- Limitations: Address any potential weaknesses or limitations of the methodology.
Each section should be clearly labeled, and the writing should be precise and concise.
12. Can you give an example of a data collection method in a quantitative thesis?
Answer: An example of a data collection method could be using a structured questionnaire to collect data on people’s attitudes toward a particular social issue. The questionnaire would include closed-ended questions with a Likert scale (e.g., 1-5, strongly disagree to strongly agree). The responses would then be quantitatively analyzed using statistical techniques like frequency analysis, cross-tabulation, or regression.
By following these guidelines, you can write a comprehensive and detailed Chapter 3 for your quantitative thesis, ensuring clarity, rigor, and a clear explanation of how the research will be conducted.